Blog
How to Test Market Demand Before a Full Product Launch
Launching a new product is exciting, but diving in without testing the market can be risky. Before investing heavily in a full-scale launch, it’s essential to gauge market demand. This step-by-step guide will help you validate your product idea, understand your audience, and ensure your product aligns with market needs.
Minimum Viable Product (MVP)
The concept of an MVP is to launch a product with just enough features to attract early adopters and validate a product idea. It allows you to test your concept’s demand without committing to a full-scale launch. In some cases, a simple website, landing page, or even a « fake » e-commerce store can serve as your MVP, depending on your industry.
Example: I once tested market demand for a niche e-commerce marketplace using a fast-built « fake » e-commerce website for a client. This setup enabled us to collect valuable insights on customer interest and pain points with minimal investment.
Key Tip: Identify the « must-have » features that address your target audience’s primary pain points. Remember, an MVP doesn’t have to be polished; it just needs to deliver core functionality.
The Advantages of Using an MVP
Using an MVP for market validation offers several benefits:
- Saves time and budget: Focus only on essentials and test before heavy investment.
- Early feedback: Gather insights to refine the product before a wider launch.
- Reduces risk: Validating demand helps ensure you’re launching a product that meets actual market needs.
MVPs are particularly valuable for startups, enabling them to launch quickly and learn on the go.
Conduct Surveys or Interviews with Target Users
Direct feedback is one of the most reliable ways to validate your market. By conducting surveys or interviews, you can ask your audience about their needs, pain points, and preferences. Use the Jobs-to-be-Done (JTBD) framework to frame your questions effectively; this framework helps you understand the specific « jobs » your potential customers need to get done.
Sample Questions:
- What problem would this product solve for you?
- What features would be most valuable?
Benefits of Surveys and Interviews:
- Understand audience needs directly from the source.
- Build initial interest in your product.
- Identify red flags early in the concept stage.
Surveys and interviews are highly actionable and provide concrete insights into market fit.
Use Social Listening to Understand Your Market
Social listening isn’t just about monitoring mentions; it’s a powerful tool for understanding demand, identifying trends, and validating your market before launch.
Why Social Listening?
Social listening lets you tap into real, unfiltered conversations. By understanding what your target audience is saying, you can spot opportunities, pain points, and unmet needs that help validate your product idea.
Start with the Right Tools
- Choose social listening tools like Brandwatch, Sprout Social, or free options like Hootsuite’s Streams.
- Set up alerts for keywords related to your niche, product, competitors, and industry trends.
Tip: Start with one or two tools to keep it manageable.
Monitor Conversations Around Key Topics
Identify the key topics and questions your audience is discussing. Look for:
- Pain points related to your product or industry.
- Features or services they feel are missing.
- Common phrases or words that indicate demand.
Example: A skincare startup might look for mentions of « sensitive skin solutions. »
Track Your Competitors
Analyze discussions around your competitors to understand where they’re excelling or falling short.
- What are customers complaining about?
- What features do users love?
- Are there unmet needs that your product could address?
Tip: Use competitor weaknesses to refine your unique selling proposition.
Identify Emerging Trends
Look out for trends in conversations over time, such as increasing mentions of certain topics, products, or needs.
- Set up trend alerts on topics relevant to your industry.
- Pay attention to growing demands for specific solutions or values (e.g., sustainability).
Pro Tip: Tools like Google Trends or Twitter’s trending topics can complement social listening.
Analyze Customer Sentiment
Sentiment analysis helps determine the general feeling about a topic or product.
- Is there positive excitement around certain features or solutions?
- Negative sentiment around pain points?
Why It Matters: Positive and negative sentiments can reveal critical areas to address in your product or messaging.
Validate Product Features and Benefits
Test interest by seeing if there’s excitement or demand for specific features.
- Identify which features resonate most by looking for enthusiastic mentions.
- Use insights to prioritize features or create messaging that speaks directly to these benefits.
Example: A food delivery startup could look for interest in « healthy meal options » or « quick delivery times. »
Gather Content and Messaging Ideas
Social listening provides insights into the language your target audience uses.
- Note popular phrases, terms, or expressions that resonate with them.
- Use these to craft messaging that feels authentic and relevant to your audience.
Tip: Use these insights for website copy, ads, and social content.
Key Takeaway: Social listening lets you validate demand, shape your product, and refine messaging—all before launching. Start listening, capture insights, and align your strategy to meet your market’s needs.
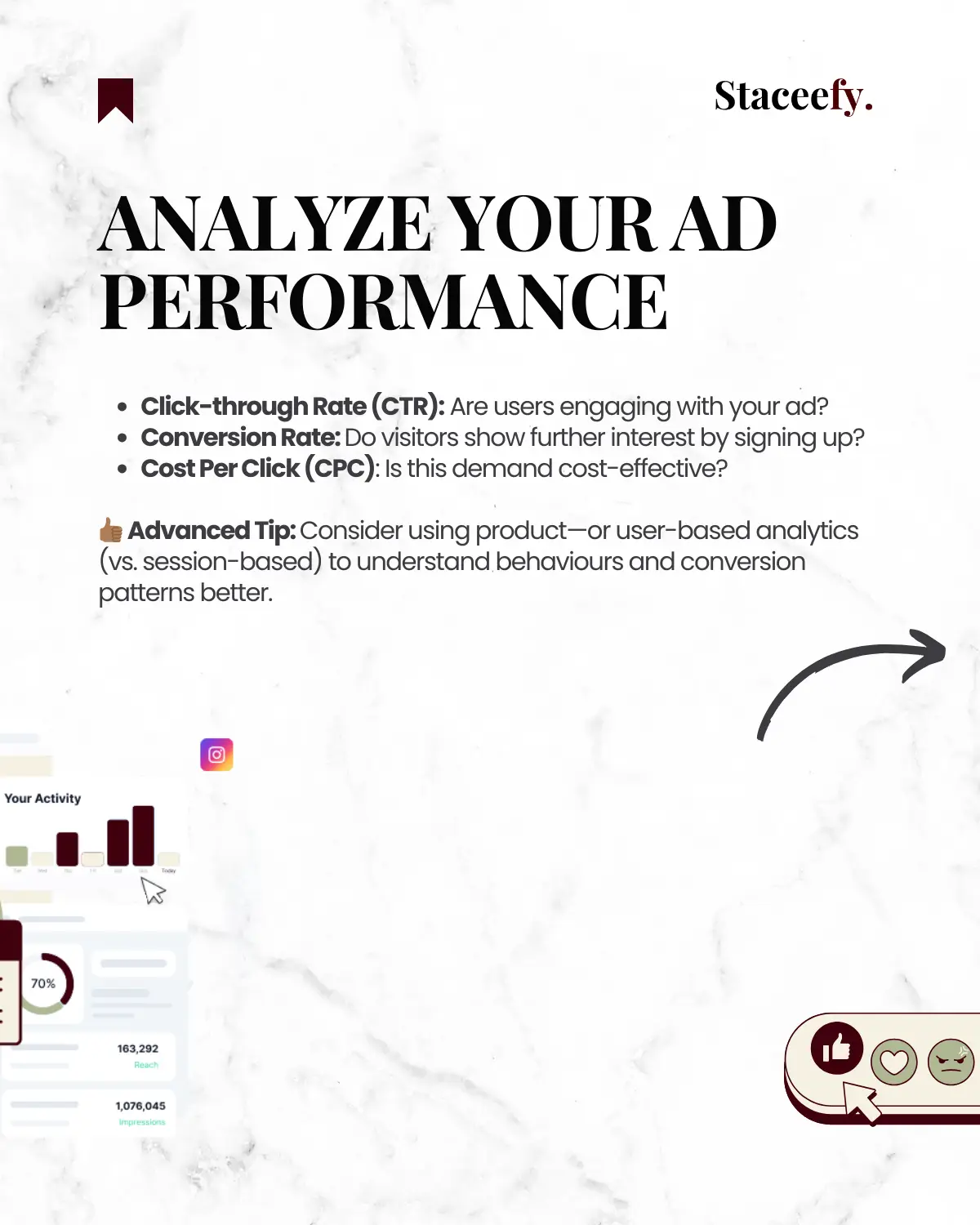
Use Paid Ads to Gauge Interest
Social media and search engine ads can help you test demand. By running small-budget ads, you can quickly assess whether there’s genuine interest in your product.
Tips for Effective Ad Testing:
- Start with a mini-research phase to identify where your target audience spends the most time, whether that’s LinkedIn, Instagram, or Snapchat.
- Use ads to direct traffic to a landing page where users can sign up for a waitlist or learn more about your product.
Metrics to Track:
- Click-through Rate (CTR): Shows if people are interested in your ad.
- Conversion Rate: Indicates if visitors are interested enough to sign up or engage further.
- Cost Per Click (CPC): Helps you gauge if demand is cost-effective to scale.
Advanced Tip: Implement product analytics or user-based analytics (as opposed to session-based) to gain a clearer picture of user behavior and any patterns in conversions.
Offer a Limited-Time Beta Release for Feedback
A limited-time beta release is an effective way to test demand and get feedback before a full-scale launch. Offer a « beta » version of your product to a small, selected group. This approach builds excitement and provides an opportunity to refine your product based on real-world use.
Best Practices for Beta Testing:
- Offer incentives (discounts or exclusive features) to encourage feedback.
- Create a feedback loop where users can share their experiences and suggest improvements.
Beta testing helps identify feature priorities, refine the user experience, and gather feedback to guide your final product adjustments.
Analyze Beta Feedback to Refine Your Product
Use the feedback gathered during beta testing to make informed changes:
- Prioritize features that resonated with beta users.
- Optimize user experience (UX) to address common pain points.
- Build a community of early adopters who can later act as product advocates.
The goal here is to fine-tune your product so that it meets your audience’s needs, reducing the chances of failure at launch.
Recommended Reads for Market Validation
These books are excellent resources if you want to dive deeper into market validation strategies:
- “The Lean Startup” by Eric Ries: A foundational guide for building businesses and products with an emphasis on rapid experimentation.
- “The Lean Product Playbook” by Dan Olsen: Provides a step-by-step process to create products that customers love.
- “Inspired: How to Create Tech Products Customers Love” by Marty Cagan: Focuses on effective product management and building what customers truly want.
- “Sprint: How to Solve Big Problems and Test New Ideas in Just Five Days” by Jake Knapp, John Zeratsky, and Braden Kowitz: A practical guide to rapid prototyping and testing ideas in a compressed time frame.
- “Value Proposition Design: How to Create Products and Services Customers Want” by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneu